gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.socialHere's something fun, who wants to guess what this is?
penguin42
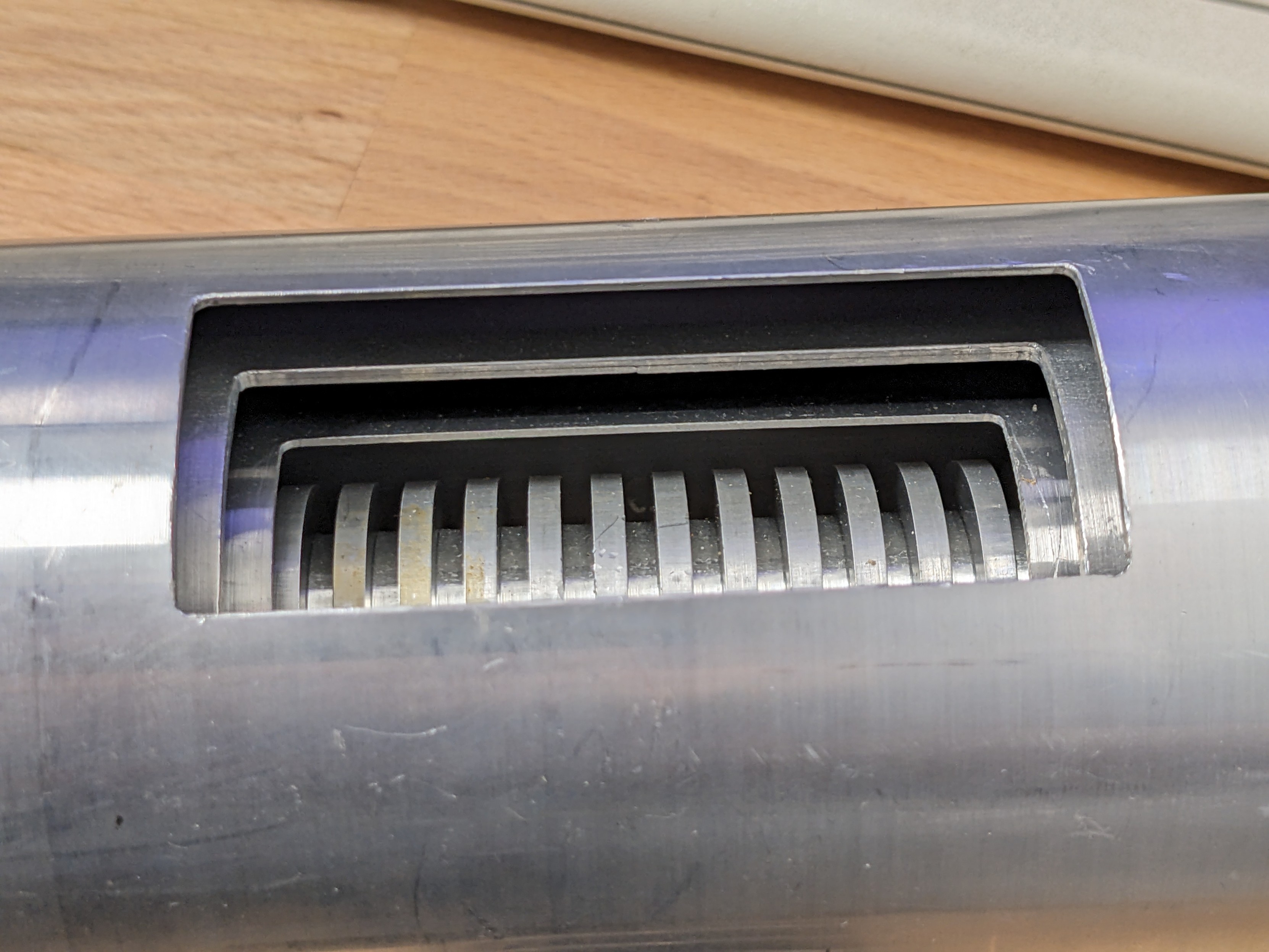
penguin42@mastodon.org.uk@gigabecquerel The inner part looks like a shredder to me, but then what it's doing inside 3 tubes I dunno.
@gigabecquerel Für was mit Mikrowellen würdest du eher keinen Stahl nehmen, oder?
Richard "RichiH" Hartmann
RichiH@chaos.social@gigabecquerel something without image description.
Anything.. if you're brave enough
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.socialNo correct guesses yet... none even close 😁
Hint: One of these layers is boron coated!
Benjamin Knispel
benknispel@chaos.social@gigabecquerel Boron coated sound like something with neutron detection.
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.socialDefinitely getting warmer!
Hint: It is not a "counter"
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.socialHint:
It's made to measure one kind of radiation selectively in the presence of another kind of radiation
the tower fairy
crystalmoon@chaos.social@gigabecquerel that feels like some kind of polarizing barrier, but i didn't know you could do that with waves outside the visible spectrum
Wolf480pl
wolf480pl@mstdn.io@gigabecquerel is it supposed to become hot in vacuum and then emit some atoms / ions in small quantities?
Wolf480pl
wolf480pl@mstdn.io@gigabecquerel (not sure if these binsearch-type questions are allowed but) is its purpose to emit something?
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.social@wolf480pl Emitting particles internally is part of its function, but not its purpose
Wolf480pl
wolf480pl@mstdn.io@gigabecquerel ok now I don't know if massless- (photons) and pseudo- (phonons) particles count as particles...
But assuming they do,
if emitting particles is not the purpose of this device, then maybe absorbing particles is?
Is this a type of detector?
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.social@wolf480pl Oh no no we're talking about real, massive particles here.
It is a detector!
Wolf480pl
wolf480pl@mstdn.io@gigabecquerel people were guessing 16h ago that it's a neutron detector, but you said 40min ago that no correct guesses, so it must be a something-else-detector.
Do the particles it's supposed to detect have a non-zero electric charge?
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.social@wolf480pl I never said it's not a neutron detector, just, that there were no correct guesses so far
Wolf480pl
wolf480pl@mstdn.io@gigabecquerel uhh so it could be a specific type of neutron detector... I don't know enough about neutron detectors to be able to know what types exist
gigabecquerel
gigabecquerel@chaos.social@wolf480pl The type is the interesting part!
Some clever engineering went into it to detect neutrons under the conditions it does
gigabecquerel
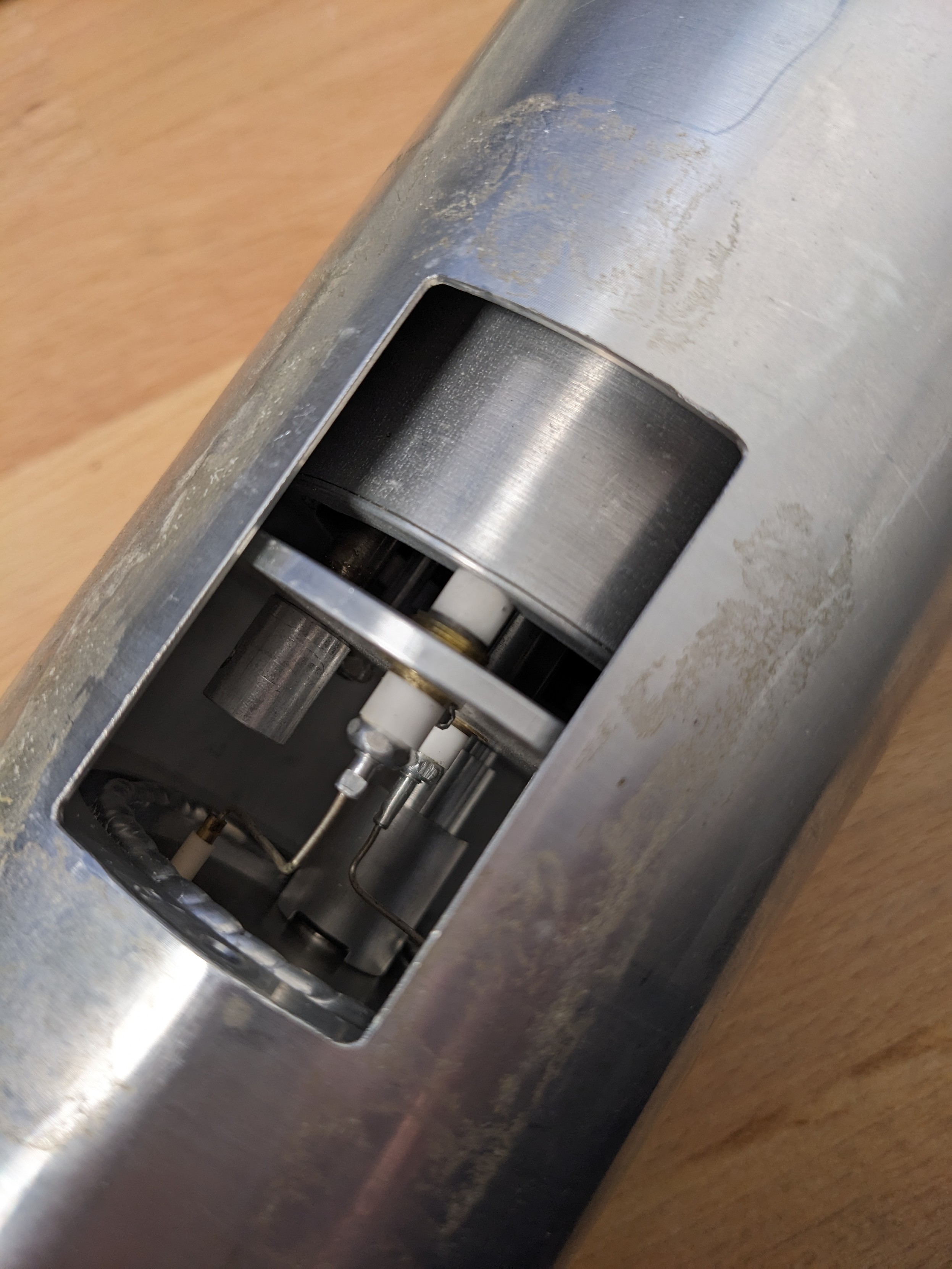
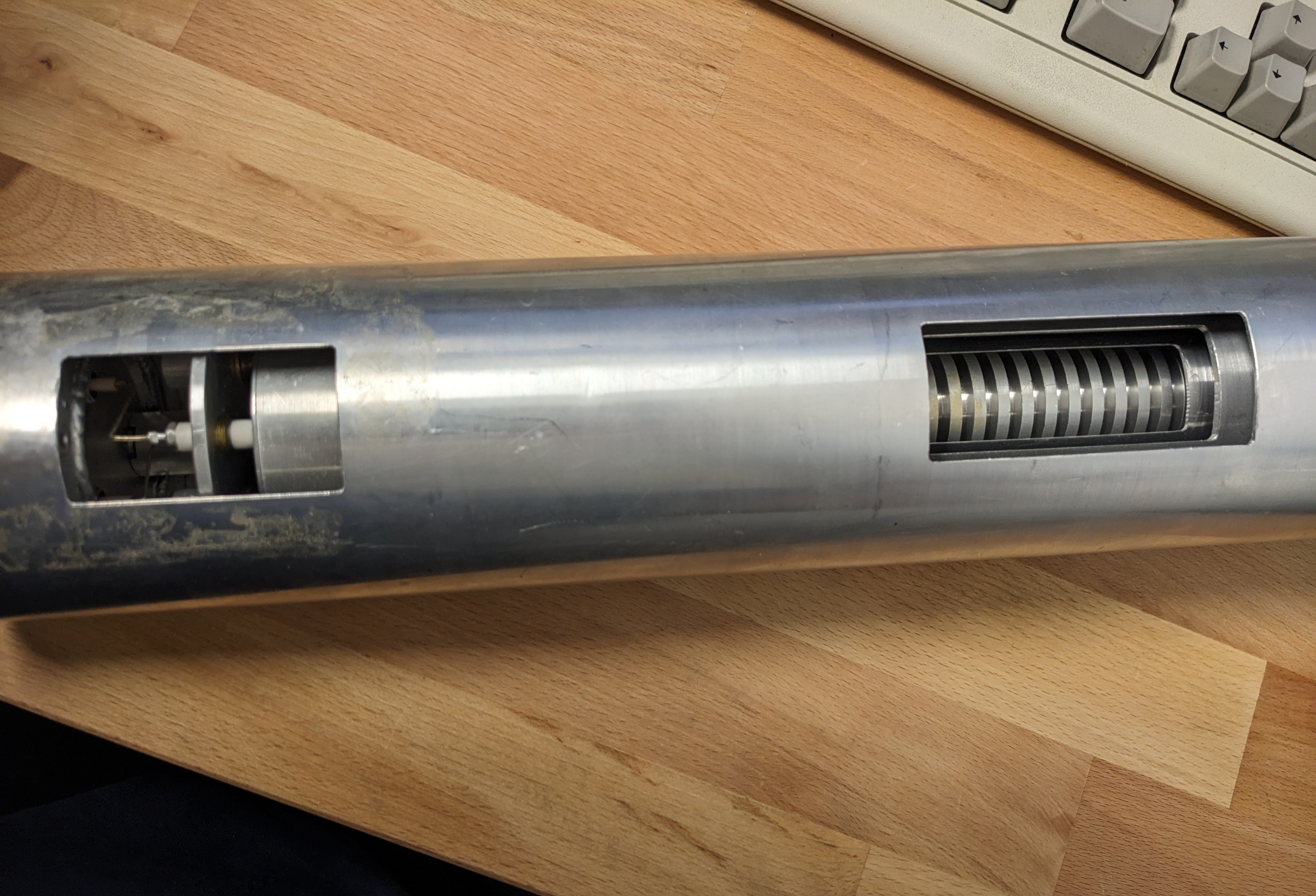
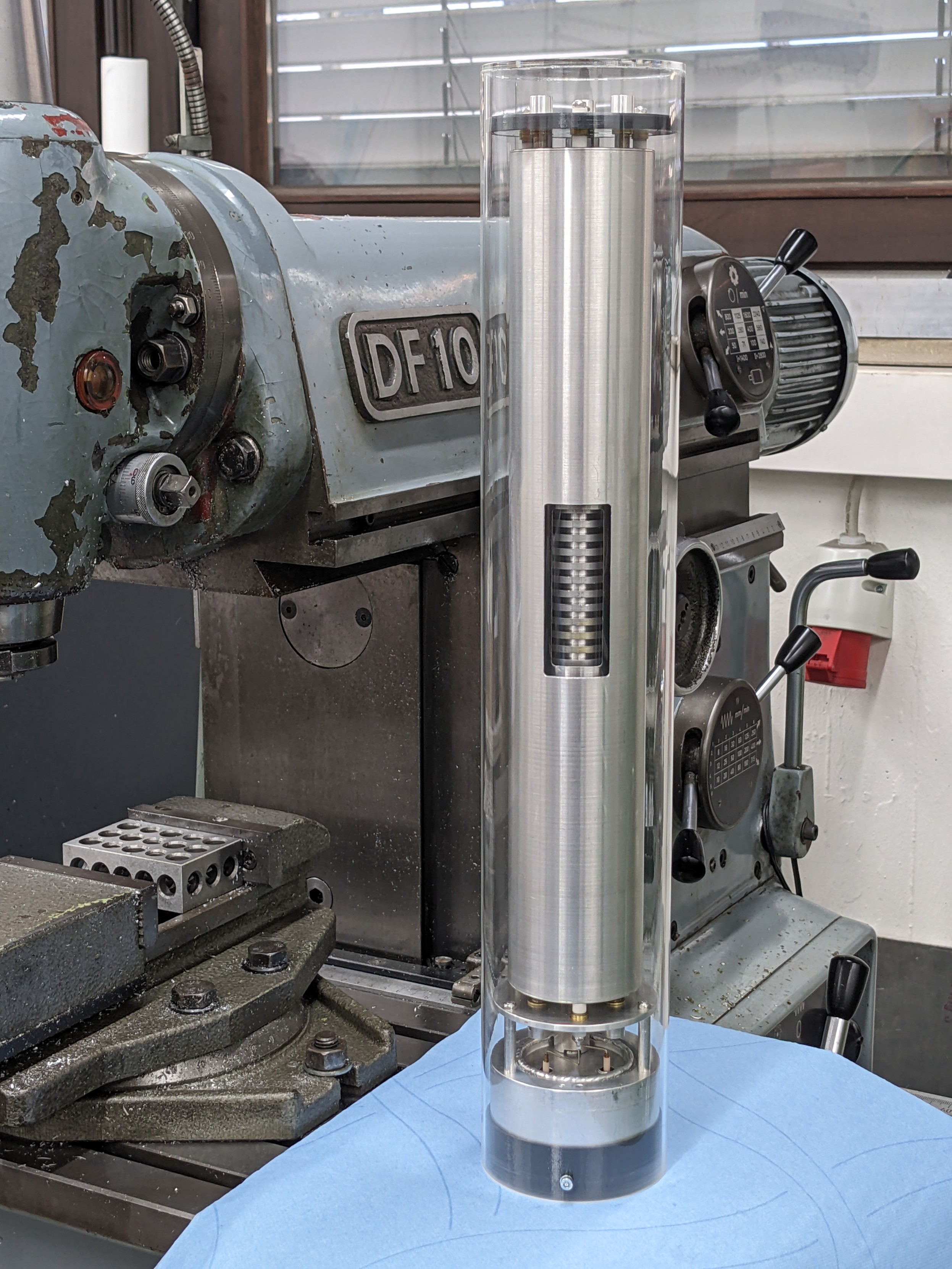
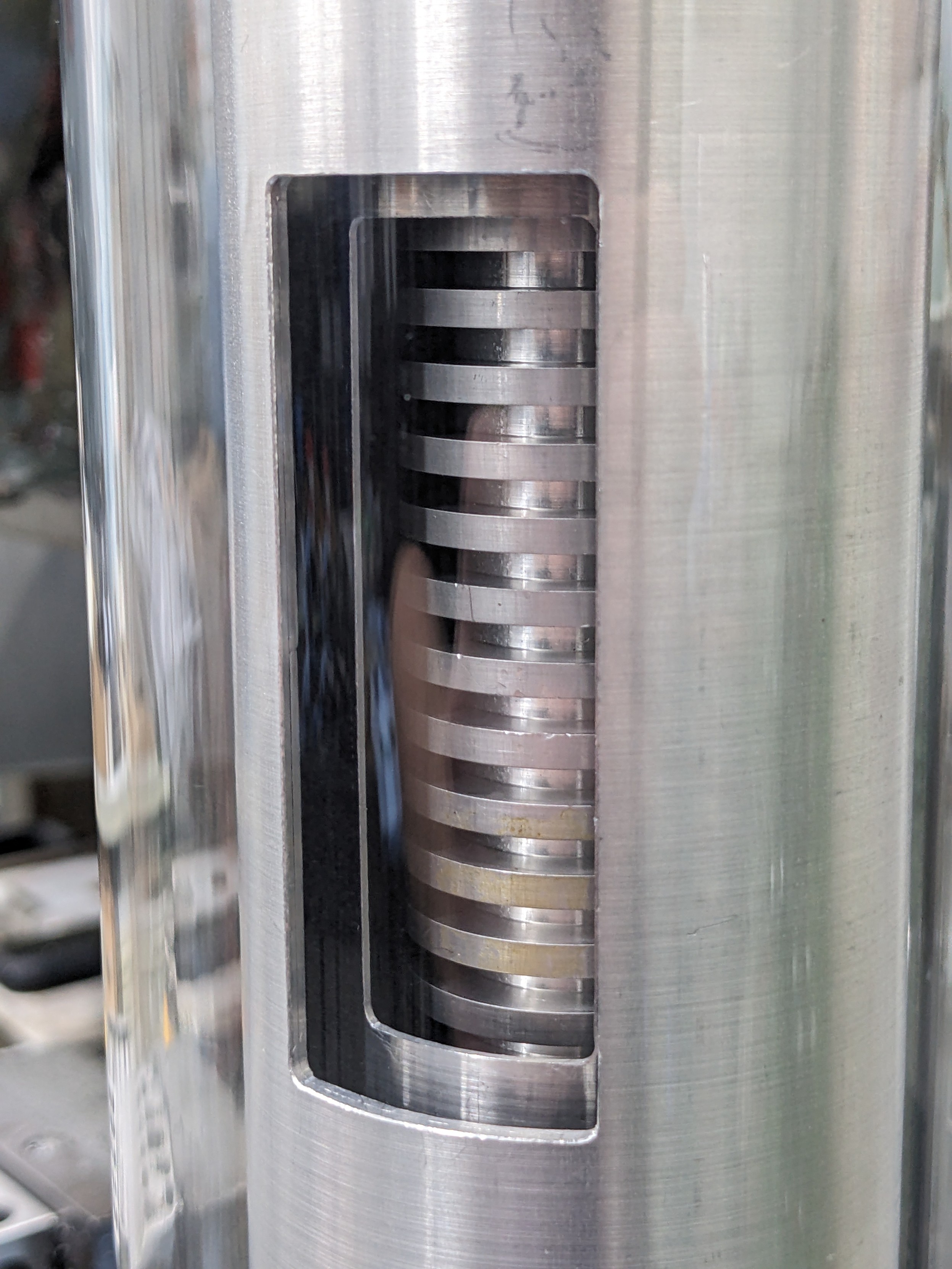
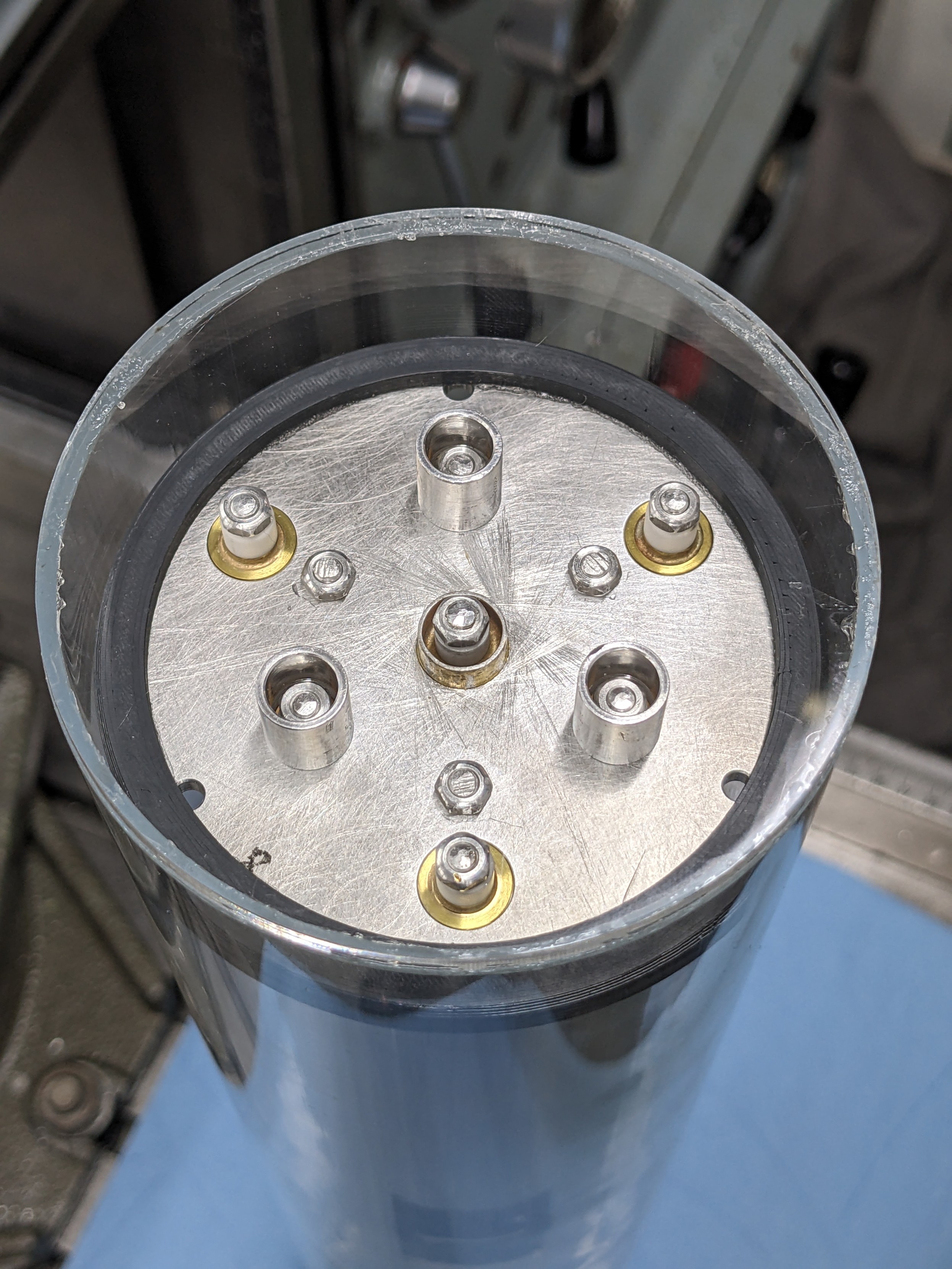
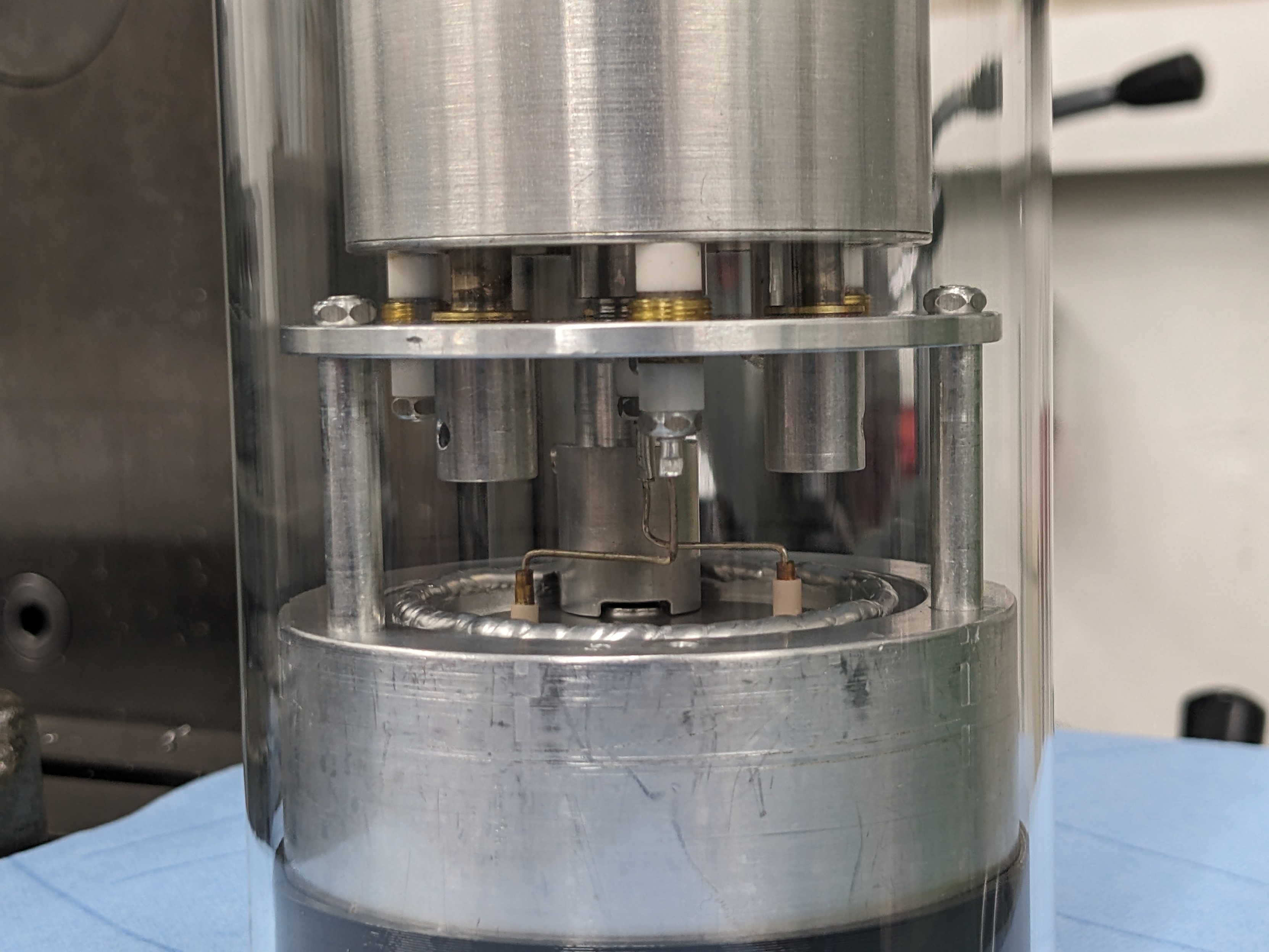
gigabecquerel@chaos.socialIt's a gamma compensated neutron ionisation chamber!
Basically two chambers in one, sharing one electrode. One chamber is coated in boron to make it neutron sensitive, the other isn't and with some clever wiring of both chambers you can make sure the current on the shared electrode is just from neutrons, regardless of the gamma background!
You'll typically find these very close to a reactor core, used for measuring power.